How Edge Computing Enhances IoT Performance
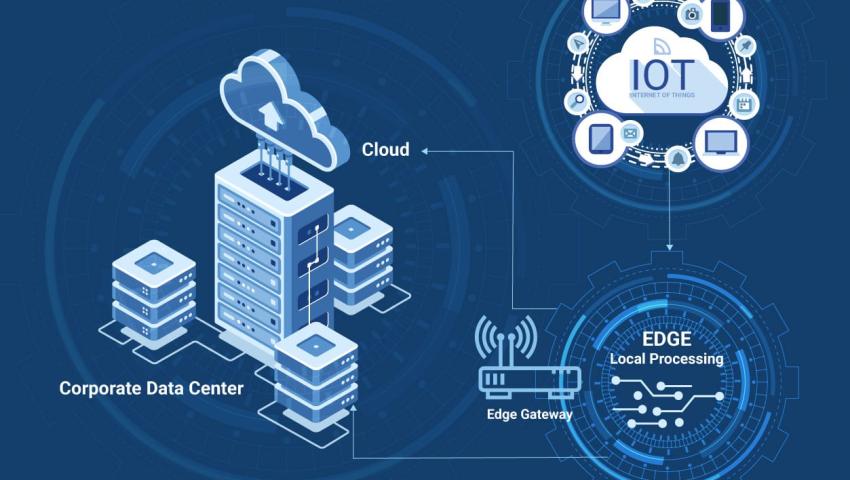
Edge computing is rapidly becoming a game-changer for the Internet of Things (IoT), enhancing its performance in ways that were previously impossible.
“Edge computing is the key to unlocking the full potential of IoT, enabling faster decision-making, enhanced security, and more efficient systems by processing data where it’s generated, not just in the cloud.”
How Edge Computing Enhances IoT Performance
Edge computing is rapidly becoming a game-changer for the Internet of Things (IoT), enhancing its performance in ways that were previously impossible. By bringing computation and data storage closer to where data is generated—at the "edge" of the network—edge computing is able to solve several of the challenges that arise from traditional cloud-based IoT solutions, such as latency, bandwidth limitations, and security concerns. Let’s dive into how edge computing boosts the performance of IoT systems.
1. Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of edge computing is its ability to reduce latency. In traditional cloud-based IoT systems, data generated by devices needs to be sent to a central cloud server for processing. This often leads to delays in data transmission and response times, which can be problematic in time-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring, or smart factories.
With edge computing, data is processed locally on the device or a nearby edge server, dramatically reducing the time it takes for the system to process information and respond to it. This real-time decision-making is crucial for IoT systems that require instantaneous feedback to function optimally.
Impact:
- Faster decision-making in critical applications like autonomous driving and industrial automation.
- More responsive IoT systems that can react in real-time without waiting for data to travel to the cloud.
2. Bandwidth Optimization
IoT devices generate massive amounts of data. If all this data were transmitted to the cloud, it could overwhelm networks and consume significant amounts of bandwidth. With edge computing, only relevant or pre-processed data is sent to the cloud for storage or further analysis. By performing some data processing at the edge, only the necessary, actionable data is transmitted, thus reducing network congestion and improving overall system performance.
This optimization of data flow is particularly important for IoT systems operating in remote locations or environments with limited network connectivity.
Impact:
- Reduced network traffic and lower data transmission costs.
- Efficient use of bandwidth, allowing IoT networks to scale without burdening the infrastructure.
3. Enhanced Security and Privacy
Security is one of the biggest concerns in IoT networks, especially as the number of connected devices grows. Sending sensitive data to a central cloud server exposes it to potential breaches during transmission. Edge computing helps mitigate these risks by processing and storing data locally, reducing the number of data transmissions to the cloud and limiting the exposure of sensitive information.
Additionally, edge computing can implement more localized security measures, such as encryption and threat detection, which are harder to bypass than centralized cloud-based solutions. The result is improved data privacy and security.
Impact:
- Localized encryption and security protocols reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Sensitive data can remain within the local network, ensuring that only essential information is sent to the cloud.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing allows IoT networks to scale more efficiently. With traditional cloud-based systems, the more devices you add, the more strain you place on network infrastructure and cloud servers. Edge computing, on the other hand, distributes the processing workload across multiple edge nodes, making it easier to manage and expand IoT systems without overloading the central infrastructure.
This decentralized model offers greater flexibility and makes it easier to integrate new devices and sensors into the system without causing bottlenecks or delays.
Impact:
- IoT systems can scale easily without compromising performance or requiring a complete infrastructure overhaul.
- New devices and applications can be integrated with minimal disruption to the existing system.
5. Improved Reliability
Reliability is a key concern for IoT systems, especially in industries where downtime can be costly or dangerous. In cloud-based IoT systems, the performance of devices is dependent on the continuous availability of a stable internet connection. If connectivity is lost, the system may fail to function properly.
Edge computing reduces this dependency by allowing IoT devices to continue operating even if they lose connection to the central cloud. Local processing ensures that the devices can perform basic functions and store data until connectivity is restored, ensuring continuous operation.
Impact:
- Reduced system downtime in critical industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and energy.
- More resilient IoT networks that can maintain functionality in the face of network disruptions.
6. Cost Efficiency
Edge computing can lead to significant cost savings in IoT networks. By processing data locally rather than sending all the raw data to the cloud, organizations can cut down on data transmission costs and reduce the need for extensive cloud storage. Furthermore, edge devices often consume less energy and require less processing power compared to cloud servers, which can lower operational costs.
Additionally, the reduced reliance on cloud computing resources can help avoid the costs associated with high cloud storage and bandwidth usage.
Impact:
- Lower operational costs associated with data storage, transmission, and cloud infrastructure.
- Reduced reliance on expensive centralized cloud services, making IoT networks more affordable to deploy and maintain.
7. Real-Time Analytics and Decision Making
Edge computing enables real-time analytics by processing data as soon as it is generated. This is particularly important for industries that require immediate insights or actions based on data, such as in healthcare, manufacturing, or security surveillance.
By analyzing data locally, edge computing reduces the need to send large amounts of raw data to the cloud for analysis. This allows for faster decision-making and quicker responses to changes in the environment, improving overall system efficiency.
Impact:
- Instant analytics lead to faster, more informed decision-making.
- Real-time responses in critical sectors such as industrial monitoring or emergency services.
Conclusion
Edge computing is a crucial advancement that enhances IoT performance by addressing challenges such as latency, bandwidth limitations, security, and scalability. By processing data closer to the source, edge computing empowers IoT devices to make smarter, faster, and more reliable decisions. As the number of connected devices continues to grow, edge computing will play an increasingly vital role in ensuring that IoT networks remain efficient, secure, and scalable.

